Historique
Analysis → History
Important part in software : the historization part, a true memory of it. It is possible in Jeedom to log any information type command (binary or digital). This will allow you, for example, to log a temperature curve, consumption, the openings of a door, etc.
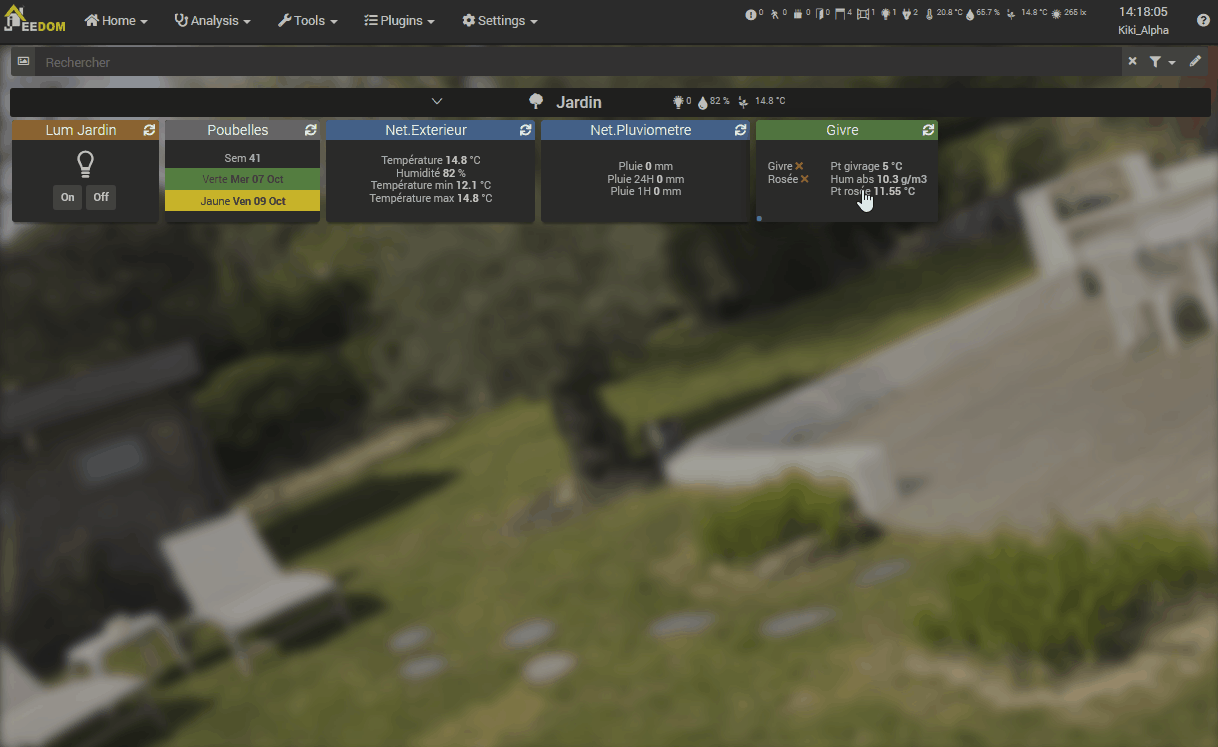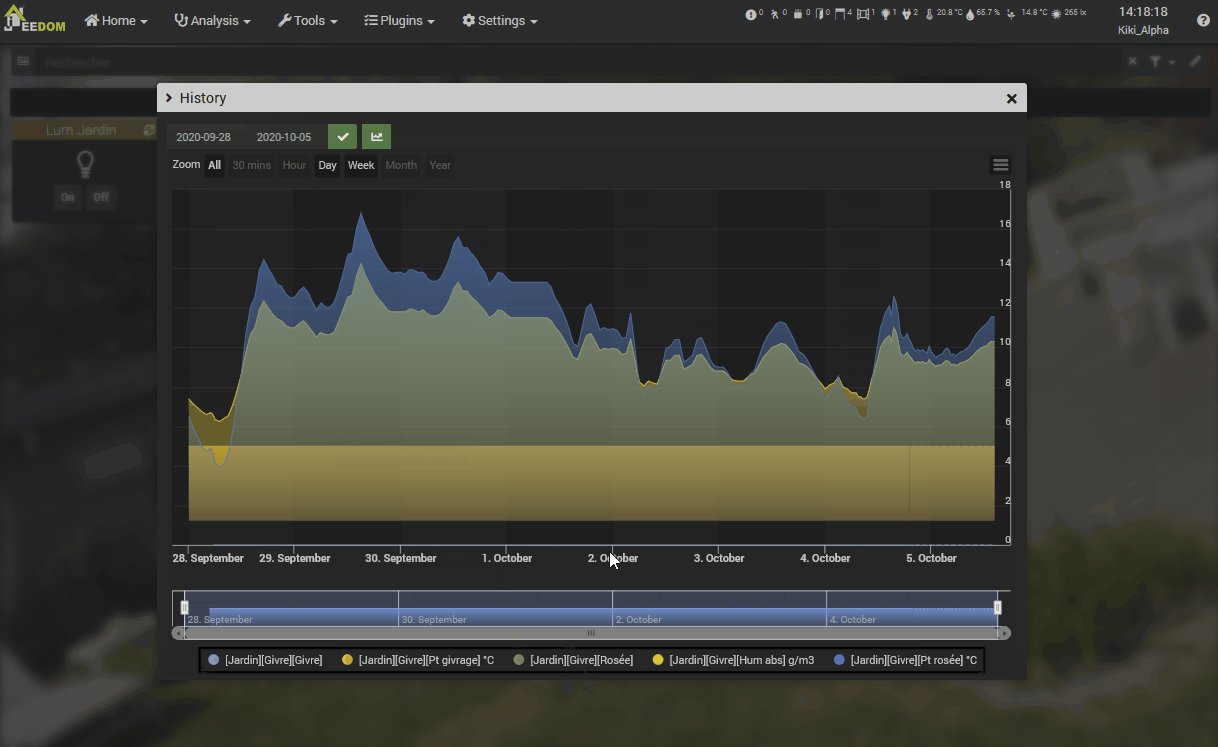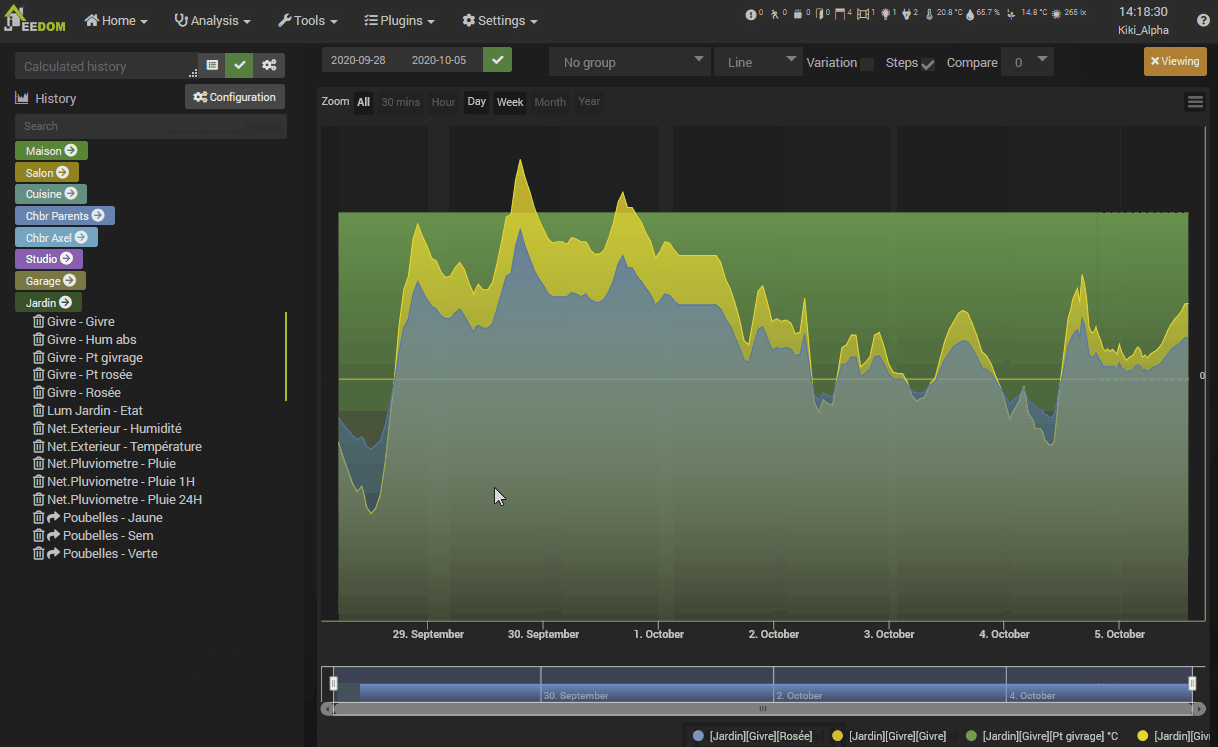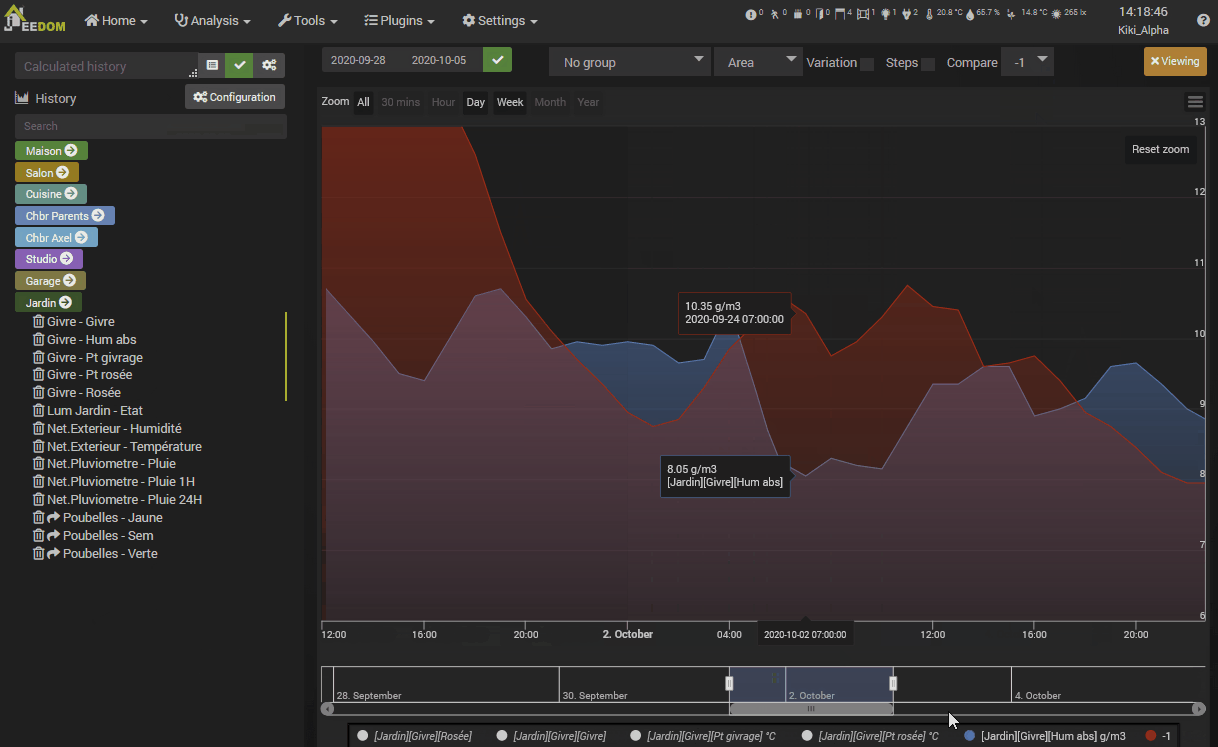
Principle of historization
Archivage
Data archiving allows Jeedom to reduce the amount of data kept in memory. This allows not to use too much space and does not slow down the system. Indeed, if you keep all the measurements, this makes all the more points to display and therefore it can considerably lengthen the times to render a graph. If there are too many points, it may even cause the graph display to crash.
Archiving is a task that starts at night and compacts the data recovered during the day. By default Jeedom retrieves all older data of 2 hours and makes 1 hour packets of it (either an average, a minimum or a maximum depending on the settings). So here we have two parameters, one for packet size and another to know when to do it (by default, these are 1 hour packets with data that are more than 2 hours old).
Tip
If you have followed well you should have a high precision on the last 2 hours only. However when I connect at 5 p.m., I have a precision on the last 17 hours. Why ? In fact, to avoid consuming resources unnecessarily, the task of archiving takes place only once a day, in the evening.
Important
Of course, this archiving principle only applies to digital orders. On binary type orders, Jeedom only keeps the dates of change of state.
Viewing a graph
There are several ways to access the history :
- By clicking on the desired command in a widget,
- By going to the history page which allows you to superimpose different curves and combine styles (area, curve, bar),
- On mobile while remaining pressed on the widget in question,
- By putting a graph area in a view (see below),
- By inserting a graph on a Design.
From Core v4.2 it is also possible to display a curve at the bottom of the tile of a device.
Historique
If you display a graph via the history page, you have access to several display options, above the graph :
- Period : The display period, including historical data between these two dates. By default, depending on the setting Display period graphics by default in Settings → System → Configuration / Equipment.
- Group : Offers several grouping options (Sum per hour, etc.).
- Display type : Display in Line, Area, or Closed off. Option saved on the order and used from the Dashboard.
- Variation : Displays the difference in value from the previous point. Option saved on the order and used from the Dashboard.
- Staircase : Displays the curve as a staircase or a continuous display. Option saved on the order and used from the Dashboard.
- Compare : Compare the curve between different periods.
Tip
To avoid any handling error, these options saved in the commands are only active when a single curve is displayed.
In the upper part where the curves are displayed, there are also several options :
On the left:
- Zoom : A shortcut area allowing you to adjust the horizontal zoom to the desired duration, if the data is loaded.
On the right:
- Visible vertical axes : Allows you to hide or display all vertical axes.
- Vertical axis scale : Allows you to activate or not the scaling of each vertical axis independently of the others.
- Grouping of vertical axes by units : Allows to group the scale of curves and vertical axes according to their unit. All curves with the same unit will have the same scale.
- Opacity of the curves under the mouse : Allows you to deactivate the highlighting of the curve when a value is displayed at the mouse cursor. For example when two curves do not have their values at the same times.
Under the curves, you can also use the contextual menu on each legend to isolate a curve, display / hide its axis, change its color, …
Graphic on views and designs
You can also display the graphs on the views (we will see here the configuration options and not how to do it, for that you have to go to the documentation of the views or designs in function). Here are the options :
Once a data is activated, you can choose :
- Color : The color of the curve.
- Type : The type of graph (area, line or column).
- Ladder : Since you can put several curves (data) on the same graph, it is possible to distinguish the scales (right or left).
- Staircase : Displays the curve as a staircase or a continuous display.
- Stack : Stack the values of the curves (see below for the result).
- Variation : Displays the difference in value from the previous point.
Option on the history page
The history page gives access to some additional options
Calculated history
Allows to display a curve according to a calculation on several commands (you can pretty much do anything, + - / * absolute value … see PHP documentation for some functions). For example :
abs(*\ [Garden \] \ [Hygrometry \] \ [Temperature \]* - *\ [Living space \] \ [Hygrometry \] \ [Temperature \]*)
You also have access to a management of calculation formulas which allows you to save them to re-display them more easily.
Tip
When you have saved calculations, these are available on the left in My Calculations.
Command history
In front of each data that can be displayed, you will find two icons :
- Trash can : Allows you to delete the recorded data; when clicking, Jeedom asks whether to delete the data before a certain date or all the data.
- Arrow : Enables CSV export of historical data.
Inconsistent value removal
Sometimes you may have inconsistent values on the graphs. This is often due to a concern with interpreting the value. It is possible to delete or change the value of the point in question, by clicking on it directly on the graph; in addition, you can adjust the minimum and maximum allowed to avoid future problems.